In Singapore, a thriving global financial hub, household income disparities have been a persistent issue that demands attention. While the city-state enjoys a high per capita income, significant disparities exist among different segments of the population. This article aims to delve into the causes and effects of household income disparities in Singapore, with a particular focus on the socioeconomic, political, and real estate implications. By understanding the underlying factors, policymakers, real estate investors, and the general public can work towards fostering a more equitable and inclusive society.
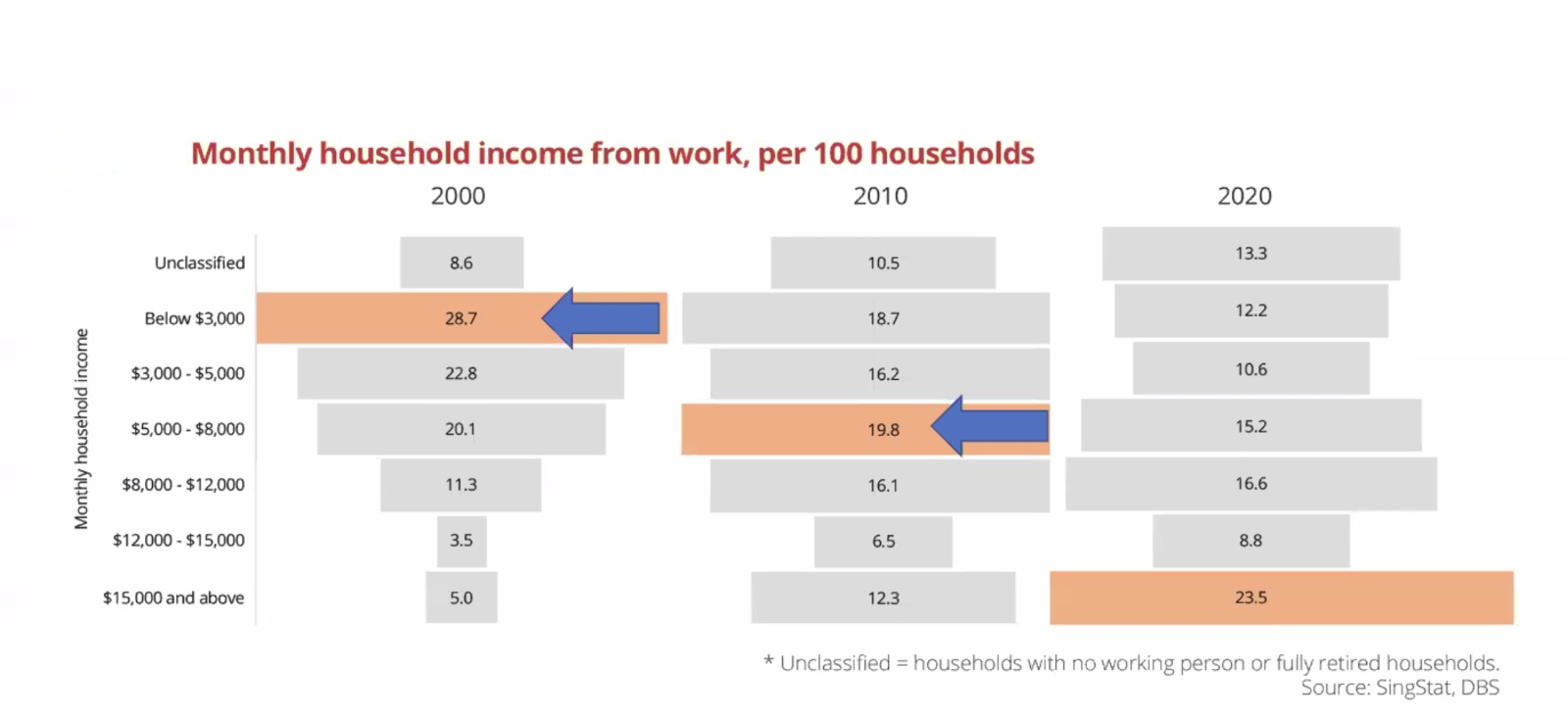
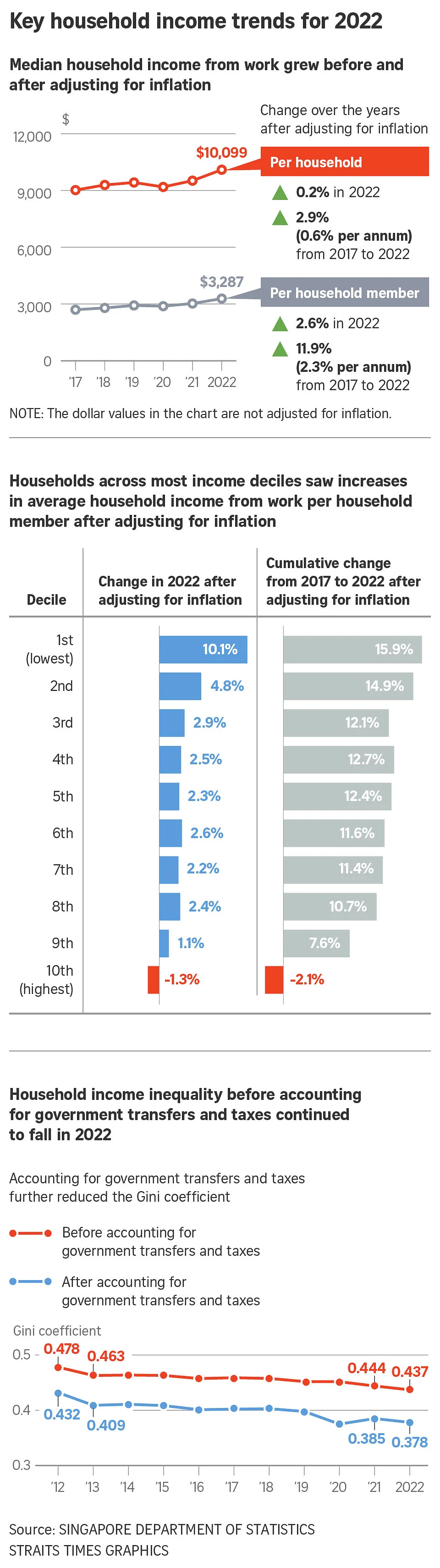
I. Causes of Household Income Disparities
1. Education Disparities
Education plays a crucial role in determining an individual’s earning potential. Singapore’s meritocratic system emphasizes academic achievements, but disparities in educational opportunities can perpetuate income inequality. Students from lower-income families may face financial constraints that limit access to quality education, resulting in reduced career prospects and earning potential.
2. Skills and Job Mismatch
Singapore’s economy is rapidly evolving, and there is a growing demand for skilled professionals in sectors like technology and finance. However, some individuals may lack the necessary skills to meet these demands, leading to a mismatch between job requirements and the available workforce. This mismatch often results in lower-paying jobs for affected individuals, exacerbating income disparities.
3. Foreign Labour Market Competition
Singapore attracts a significant number of foreign workers, who often compete with locals for jobs, particularly in low-skilled sectors. The influx of foreign labor can drive down wages in certain industries, affecting the earning potential of locals and contributing to income disparities. Additionally, some high-skilled foreign workers may command higher salaries, further widening the income gap.
4. Ageing Population and Retirement Savings
Singapore faces the challenge of an ageing population, with implications for income inequality. Older adults with inadequate retirement savings may struggle to meet their financial needs, increasing their reliance on social assistance. The lack of retirement funds can result in income disparities, as those who have managed to accumulate wealth enjoy a more comfortable retirement.
II. Effects of Household Income Disparities
1. Socioeconomic Segregation
Income disparities in Singapore can lead to socioeconomic segregation, where individuals from different income brackets reside in separate communities. Higher-income households tend to cluster in affluent areas, while lower-income households may be concentrated in public housing estates. This segregation can limit social mobility and reinforce disparities in opportunities and access to resources.
2. Reduced Social Cohesion
High levels of income inequality can erode social cohesion, as individuals from different income groups may have limited interactions. This lack of social integration can create a fragmented society, with limited empathy and understanding between different socioeconomic groups. This, in turn, can hinder efforts to address income disparities and create a more inclusive society.
Strain on Public Resources and Social Welfare
Income disparities place additional strain on public resources and social welfare systems. Lower-income households may require more support from government initiatives, including subsidized healthcare, education, and housing. The burden on the state to address these disparities can impact the allocation of resources, potentially affecting other sectors such as infrastructure development and public services.
III. Implications for Real Estate Market
1. Housing Affordability Challenges
One of the most significant implications of household income disparities in Singapore is the impact on the real estate market, particularly housing affordability. Higher-income households have greater purchasing power, enabling them to afford private properties in desirable locations. This increased demand drives up property prices, making it more challenging for lower-income households to access suitable housing options.
2. Rising Income Disparities and Property Market Disparity
As income disparities widen, the real estate market tends to mirror these disparities. The demand for high-end luxury properties may surge, while the affordability of housing for the lower-income segment diminishes. This disparity in the property market perpetuates income inequality and limits opportunities for upward mobility, as property ownership is a key wealth accumulation avenue for many Singaporeans.
3. Impact on Rental Market
Lower-income households often rely on the rental market for housing. As income disparities persist, these households face challenges in securing affordable rental options, particularly in desirable locations. Rising property prices and rental rates can lead to housing insecurity, forcing some individuals and families to live in substandard conditions or rely on public housing assistance.
Conclusion
Household income disparities in Singapore stem from a complex interplay of factors, including education disparities, skills mismatch, foreign labor market competition, and retirement savings challenges. The effects of income disparities are far-reaching, impacting socioeconomic segregation, social cohesion, and public resources allocation. Within the real estate market, housing affordability challenges, property market disparity, and the impact on the rental market are key implications.
To address these disparities, a multifaceted approach is needed, encompassing improvements in education and skills development, targeted social welfare programs, and policies that promote inclusive growth. Real estate investors and policymakers must play a role in fostering a more equitable society, ensuring access to affordable housing and promoting initiatives that bridge income gaps. By working together, Singapore can strive towards a society that offers equal opportunities and a higher quality of life for all its residents.
